If you enjoy the delicious taste of coffee, you’re not alone.
In fact, a study published in the Journal of Nutrition shows about 154 million Americans enjoy drinking coffee on a regular.
Surprising, right?
Well, have you ever wondered – is there more to coffee than just caffeine? And why do many love it so much?
In this post, I’ll be discussing the WHATs and WHYs concerning coffee’s euphoric effects.
Stick around to find out more!
Table of Contents
Quick Overview: Understanding the Role of Caffeine in Coffee
Typically:
The first ingredient likely to pop up in your mind when thinking of coffee is caffeine. And that is understandable…
Caffeine is one of the major ingredients present in coffee.
However:
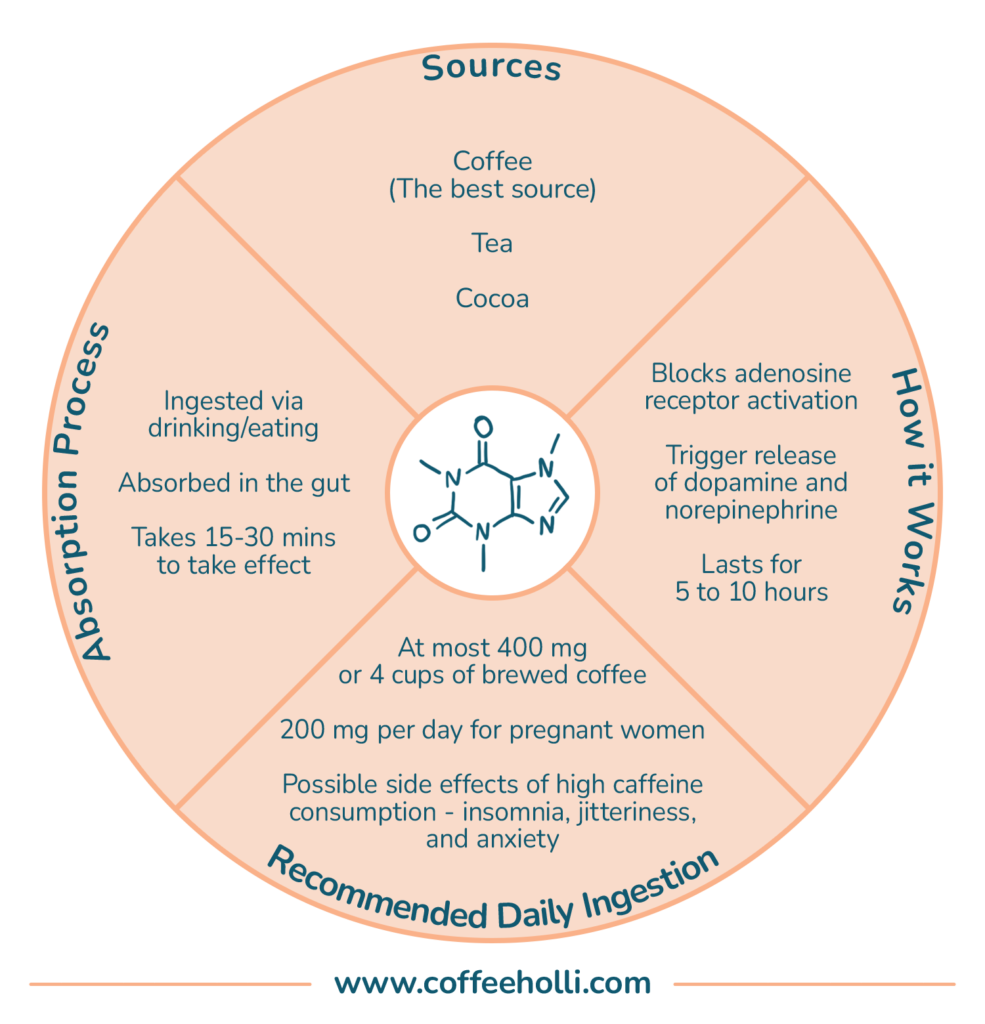
It isn’t solely in coffee. You can also find this ingredient in natural products like tea and cocoa; in varying amounts.
Or in manufactured items including chocolate, soft drinks, and energy drinks.
Examples…?
The image below shows the caffeine content of popular caffeinated drinks; as curated from the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
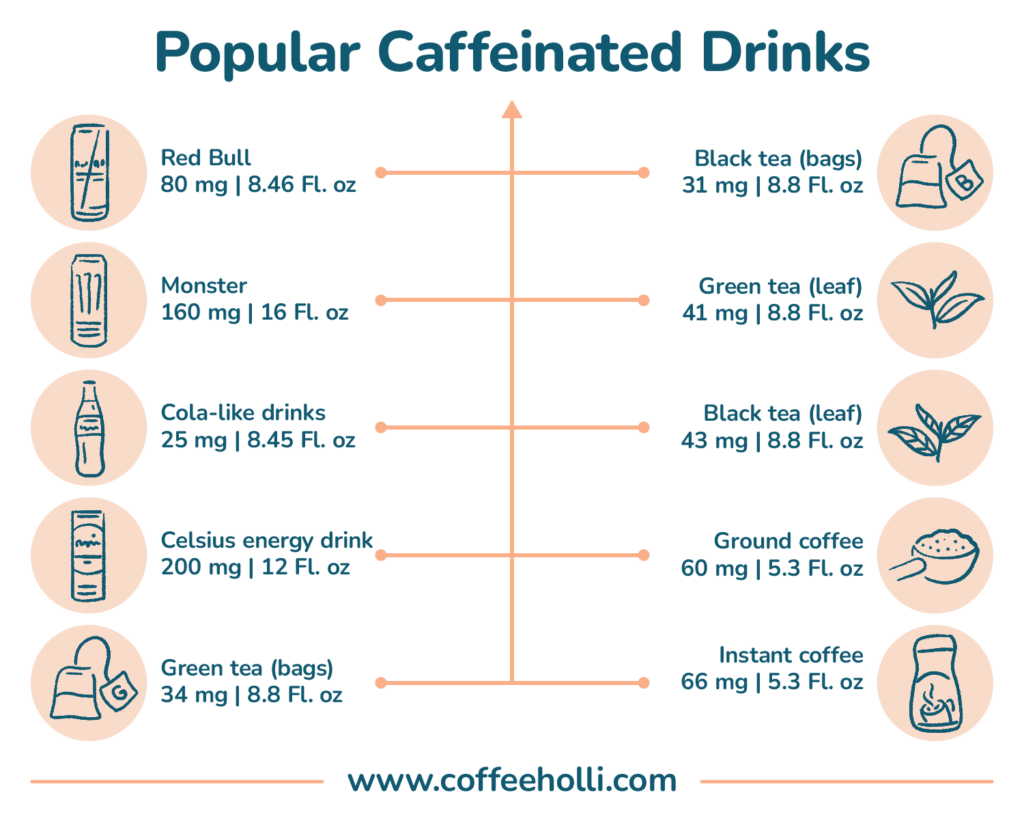
Additionally:
Caffeine is sometimes used in manufacturing certain drugs. In some cases, it is even recommended to enhance weight loss and treat migraines.
According to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), about 80 % of adults in America consume caffeine daily.
Of course:
Seeing how versatile this substance is, the billion-dollar question now becomes, “what is caffeine, and how does it work?”
Well…
What Exactly Is Caffeine and How Does It Work?
I know we can all relate to this simple fact.
It’s hard to wake up energetic in the morning. And you’ll continue to be sluggish and blurry-eyed until you get a few sips of coffee into your system.
Right?
Well, that is what many call the caffeine kick.
But how exactly does coffee make people less foggy and more alert?
You see:
Caffeine is a natural stimulant.
And a lot of us love it for its ability to boost alertness, increase brain activity, and improve attention. Plus, it tends to make one feel energetic.
How does it work?
Well:
After having a cup of coffee,the caffeine is quickly absorbed from your gut and into the bloodstream. It then dissolves into your body’s fat molecules and water before being transported to your brain.
Amazingly:
This entire process takes place fast.
Based on a paper published by the National Library of Medicine, caffeine is completely absorbed 45 minutes after being ingested.
However, studies have also shown that its stimulating effectstend to kick in around 15 minutes after ingestion.
Note:
Caffeine can remain in your bloodstream for about five to ten hours. Thus, keeping you alert and active for most of the day is a possibility.
However:
With time,the jolt of energy gradually dissipates; slowly returning your body to its default mode.
How Exactly Does Caffeine Affect Your Brain and Body?
Well:
Caffeine is widely known to be a natural stimulant, but…
How does it stimulate your brain and body? Or better yet, how does caffeine boost your energy and focus?
Well:
According to Dr. David Juurlink, caffeine stimulates your body by countering the effects of a compound called adenosine.
Get this…
Adenosine is considered to be a depressant when it acts on the nervous system. Overall, it slows down the activities of the central nervous system and promotes sleep.
Now:
Since caffeine counters the effect of adenosine, it can make you feel energetic and focused rather than tired and sleepy.
How does this work?
Well, during this process, caffeine encourages the release of adrenaline. And that explains the energy boost you feel after a cup of coffee.
It also increases the levels of a hormone called dopamine; widely known for its “feel-good” effect.
Of course:
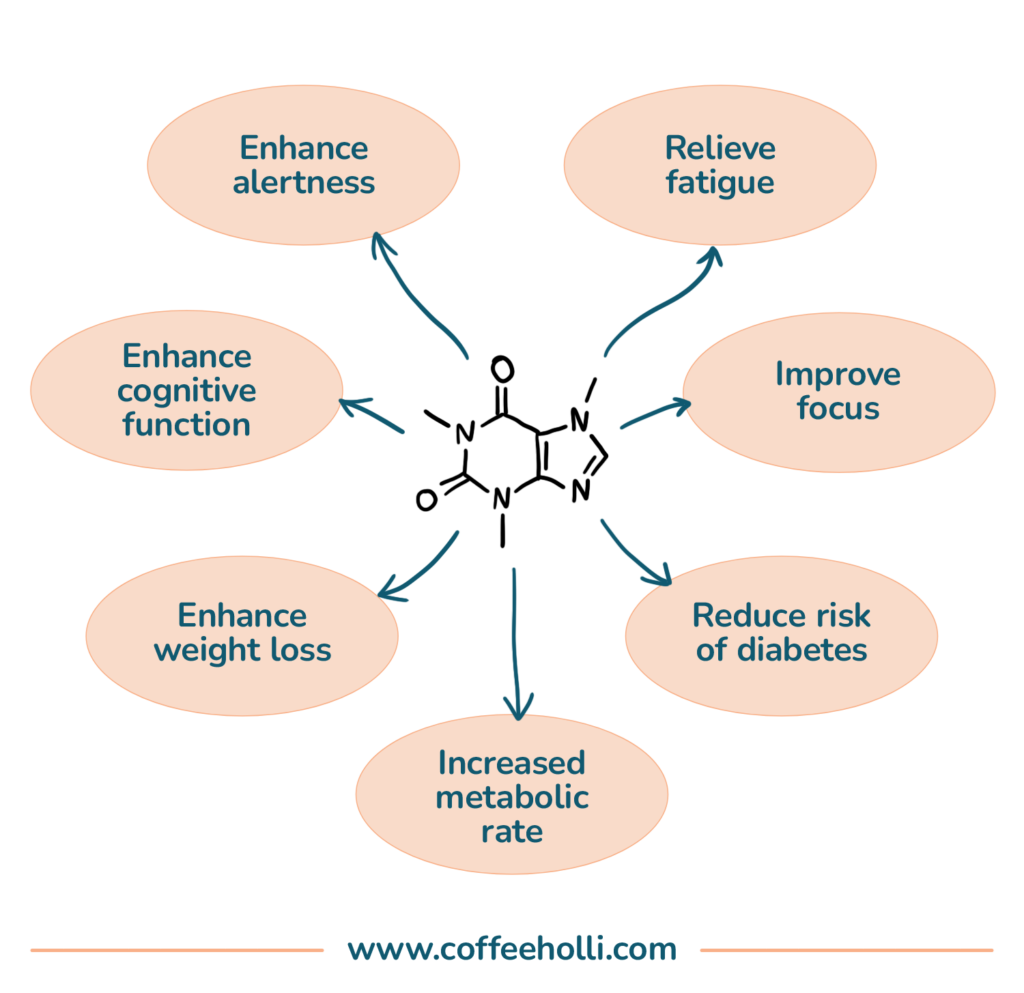
Aside from its euphoric effects and the jolt of adrenaline released, caffeine also provides numerous health benefits.
For example…
Unfortunately, There Are Also Side-Effects of Too Much Caffeine
Here’s a fact:
Too much of anything could become toxic, regardless of how good it is.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, the recommended daily dose of caffeine for healthy adults is 400 mg. This is equivalent to about four medium-sized or three 8-oz cups of coffee.
When consumed excessively, caffeine causes:
- Dizziness
- High blood pressure
- Insomnia
- Increased anxiety
- Jitters
- Headaches
Fun fact:
Caffeine is regarded as a drug.
As such, tolerance for it tends to increase with time. Thus, it can cause unhealthy dependence.
This gradually forces users to increase their daily consumption; eventually, leading to withdrawal symptoms.

All the same:
When consumed in the appropriate quantity, coffee can be a great way to get a nice jolt of energy.
Exploring the Unknown: Role of Other Constituents in Coffee
Unsurprisingly:
Caffeine isn’t the only constituent present in coffee, just as cocoa isn’t the only ingredient used to manufacture chocolate.
Several other compounds alongsidecaffeine contribute to the euphoric effect coffee has on a person.
Interesting, right?
You see:
These compounds affect the quality, taste, and aroma of the coffee you consume daily.
And as buttressed by a nutritionist, Kimberly Gomer, several of the health benefits coffee drinkers enjoy are a result of these compounds.
As such:
It’s important to know what other compounds are in your morning dose of java and what effects they have on you.
A Look at the Other Compounds That Make Up Coffee and What Each Does
Fun fact:
A study published in the National Library of Medicine showed thatthe chemical composition of coffee extensively affects its aroma and biological functions.
While this might be extremely complex, it often varies depending on factors such as the type of coffee and growing conditions.
Nevertheless:
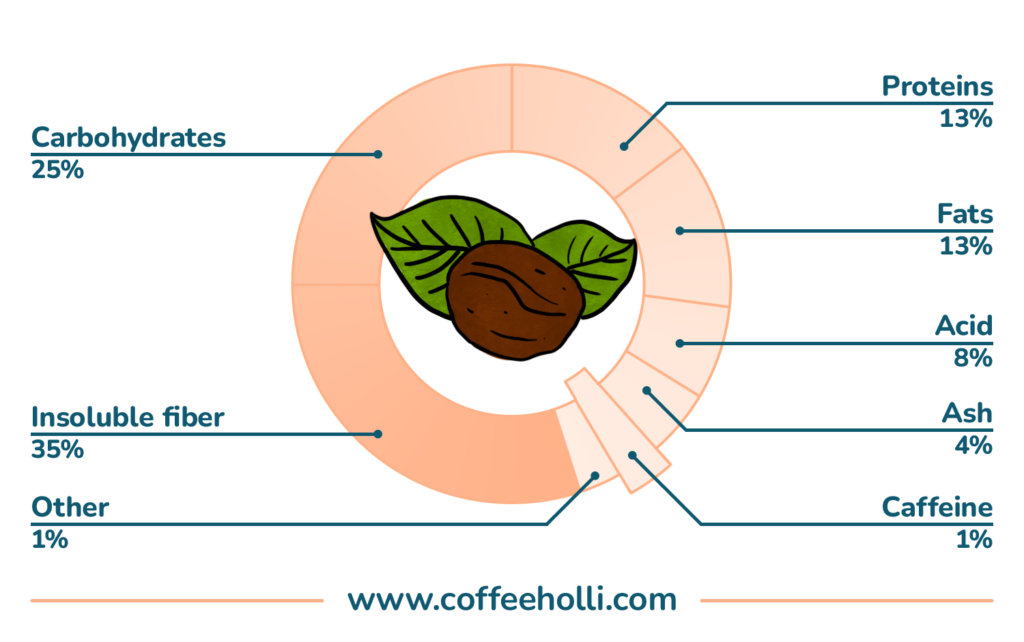
The major constituents in most coffee beans include:
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Acids
- Lipids
- Alkaloids
- Minerals
- Aromatic compounds
But:
Remember, their actual number and concentration do differ in different types of beans.
For example…
The table below shows the composition of components in Arabica and Robusta coffee based on a study conducted by the researcher, Niya Wang.
| Component | Arabica Coffee (%) | Robusta Coffee (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Polysaccharide | 40.8 | 54.4 |
| Sucrose | 8.0 | 4.0 |
| Reducing sugars | 0.1 | 0.4 |
| Other sugars | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| Lipids | 16.2 | 10.0 |
| Proteins | 9.8 | 9.5 |
| Amino acids | 0.5 | 0.8 |
| Aliphatic acids | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| Quinic acids | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Chlorogenic acids | 6.5 | 10.0 |
| Caffeine | 1.2 | 2.2 |
| Trigonelline | 1.0 | 0.7 |
| Minerals (oxide ash) | 4.2 | 4.4 |
| Volatile aroma | traces | traces |
| Water | 8 to 12 | 8 to 12 |
1. Carbohydrates
Get this:
Carbohydrates (Polysaccharides) are the major constituents of coffee, as they account for up to 60% of its composition.
Generally, these carbohydrates play several vital roles in determining the properties of coffee.
For instance:
A study posted on the National Center for Biotechnology Information reveals that carbohydrates in coffee affect the aroma and character of the final brew.
How?
Well, carbohydrates are generally associated with sweetness.
While coffee typically has a discernable bitter taste, carbohydrates facilitate the subtle sweet undertones you may notice.
Furthermore:
The carbohydrate component of a coffee bean reacts with Amino Acids at 140 degrees Celsius to produce a Melanoidin compound.
This compound is responsible for the deep brown shade noticeable in roasted coffee beans.
Note:
Caramelization also occurs during roasting.
Both reactions leave behind a noticeably sweet, charred aroma and taste. The same occurrence is observable in charred meats and baked pastries.
2. Proteins
Here’s the thing:
Although the protein content in coffee is much smaller than the carbohydrate content, it is still considered to be a vital constituent.
According to a study by researchers Mazzafera, Schimpl, and Kiyota, the protein found in coffee beans predominantly affects the quality of coffee.
Here’s why:
Proteins produce Amino acids when they are broken down. This facilitates the reaction that produces the Melanoidin compound.
Therefore:
Protein is equally responsible for the sweet, charred taste and aroma that’s unique to well-roasted coffee beans.
3. Acids
Acidity is a significant property that affects the flavor of coffee produced and also determines the effect of coffee on the body.
Some of the acids present in coffee include:
- Citric Acid
- Chlorogenic acid
- Phosphoric acid
- Formic acid
- Lactic acid
Typically:
Acids are mostly formed during roasting.
Much like the acidity in wine, these compounds add a positive spin to the taste of a coffee brew. Generally, acidity gives coffee the characteristic tartness felt on the tip of your tongue.
Also:
Acidic coffee will leave a strong, pleasant after-taste at the back of your mouth.
4. Lipids
The concentration of lipids or fat in coffee relies heavily on the species of coffee bean.
Usually, the lipids present in coffee are made up of Sterols, Diterpenes, Diterpenes Esters, and Triacylglycerol.
Interestingly:
A study was done on the role of lipids in flavors. It primarily showed lipids as the precursors that set up flavor profiles by reacting with other compounds.
Notably:
A high enough lipid concentration can alter existing flavors in your coffee. It can either be positive, like the flavors observed in cheese, or negative, like with aged milk.
5. Alkaloids
Ordinarily:
The major alkaloids present in coffee consist of two major compounds, which are caffeine and trigonelline.
As I’ve mentioned, caffeine’s role in coffee is centered around its ability to stimulate the central nervous system.
On the other hand:
Trigonelline is an alkaloid whose concentration in coffee is much smaller compared to caffeine. However, its effect on the overall quality of coffee cannot be overlooked.
To support this:
A study published by the Royal Society of Chemistry showed that trigonelline contributes to coffee’s bitter taste and aroma.
Caffeine has a similar taste and aroma but tastes slightly soapy on its own.
6. Minerals
Here’s the thing:
Although the composition of minerals in caffeine is very minute, it still substantially affects the quality of coffee. Some minerals occur in large quantities, while others only occur in traces.
Keep in mind:
Minerals mostly affect the nutritional value of coffee. The change in flavor notes based on mineral concentration in the coffee bean isn’t typically noticeable.
However:
A study published in an ACS publication shows the role of mineral-rich water in brewing. It helps better extract the rich, bitter and subtly sweet flavors associated with a good cup of coffee.
7. Aromatic Compounds
The aromatic compounds in coffee make your coffee smell the way it does.
However:
These compounds are considered to be volatile.
Smell and taste are inclusive senses, with one typically coercing the other. In this case, aromatic compounds can add to the richness of your coffee.
For instance:
Furans are aromatic compounds that add a caramel note to your coffee. While compounds like Guaiacol produce a smoky, almost spicy scent and taste.
The Health Benefits of Coffee’s Compounds…?
Of course:
Based on the info above, it’s clear that all the compounds present in coffee substantially affect its overall quality and taste.
Unique coffee flavors are often due to varied concentration levels of these compounds in different types of coffee.
That said…
Have you ever wondered – does coffee have health benefits?
Well, Harvard’s School of Public Health gives an assertive – YES. If taken in the right quantities, coffee’s compounds can boost your overall body health, mood, and well-being.
How?
Here are a few examples…
1. Antioxidant Activity
In simple terms, antioxidants protect you from cancer, diabetes, and heart diseases.
What’s more?
Most of the antioxidant activity coffee exhibits are majorly due to its other compounds aside from caffeine.
Now:
According to an NCBI study, coffee’s antioxidant activity is strongly related to melanoidins. That are formed from the reaction between carbohydrates and protein during roasting.
Also, compounds like chlorogenic acid and trigonelline are considered to be effective antioxidants.
Fun fact:
The NCBI also asserts that coffee is among the largest sources of antioxidants consumed in the U.S.A.
2. Neuroprotection
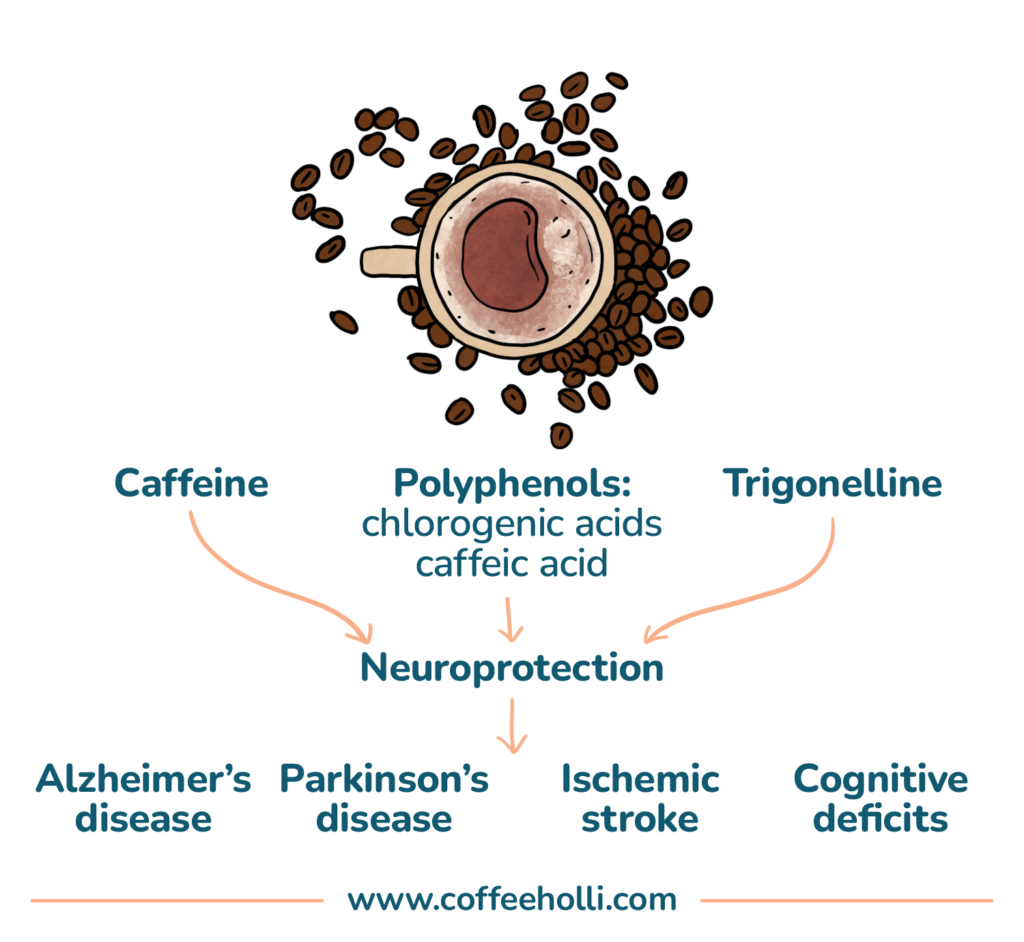
Get this:
Aside from being a great source of antioxidants, coffee can also prevent neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s.
Now:
Although the neuroprotective tendency of coffee is typically attributed to caffeine, it isn’t always the case.
A study by researchers Saud and Salamatullah shows that compounds like chlorogenic acid can also provide neuroprotection.
3. Anti-inflammatory Benefits
Another excellent health benefit you enjoy by drinking coffee is the anti-inflammatory benefits its constituents have on your body.
In brief:
Substances with anti-inflammatory properties tend to reduce pain and swelling.
However:
Did you know that coffee’s anti-inflammatory activity is also great for your mental health?
Well:
According to the National Coffee Association, people who battle depression typically havehigh concentrations of inflammatory-related protein in their blood.
And:
Since coffee provides anti-inflammatory perks, it effectively decreases the risk of depression. This explains why you tend to feel great after your morning dose of coffee.
4. Antidepressant Activity
Here’s a fact:
Studies have shown that coffee’s anti-inflammatory properties can boost mental health and thus decrease the risk of depression.
Surprisingly, this property isn’t the only reason coffee’s great for your mental health.
You see:
Nutrition Specialist, Blanca Garcia, recently explained that some of the compounds in coffee such as diterpene and trigonelline also act as antidepressants.
Awesome, right?
Why Do People Enjoy Coffee So Much? – Its Effects on Mood and Behavior
Get this:
So far, I’ve explained the effects the various compounds in coffee have on your body. I’ve also explained how they all work together to produce coffee’s overall “feel-good” effect.
So:
Is there more to this?
Yes. Let’s dive into how daily routine and social aspects of coffee drinking can improve your mood and well-being.
The Flavor Factor: Do the Taste and Aroma of Coffee Affect Your Mood and Behavior?
Without a doubt:
Taste and smell are extremely important stimuli.
They work together to produce what you perceive as flavor and influence how much you enjoy meals and drinks.
Think about it for a second:
Have you ever walked past a bakery and felt the urge to stop and buy something (even when you’re not hungry)?
Well:
According to the Institute of Culinary Education, most bakeries rely heavily on the scent emanating from their ovens to trigger your response.
Interesting, right?
The same scent-appeal applies to coffee.
Remember:
The various compounds in coffee stimulate your brain, make you feel alert, and encourage the release of dopamine; which tends to make you happy.
Therefore, when you smell and take your first sip, it automatically triggers fond memories.
For example:
Memories of the blissful feelings or fantastic rush you often feel after a fresh, nicely-brewed cup of joe. This encourages your brain to release dopamine.
Which, in turn, makes you feel happier.
Bottom line?
A nice, aromatic, and flavorful cup of coffee can greatly improve your mood and behavior.
Social Effects: Coffee as a Participation Enhancer
Coffee is a popular drink. It often features in office breakrooms, meet and greets, business meetings, get-togethers, etc.
Why?
Because coffee gives us that extra kick of energy we need to get the job done.
But:
Could it also improve the quality of our involvement?
This is the premise of an article published on the University of Oxford school website.
The setting?
Small group discussions held by university students. Each group was given a topic to discuss. Half of the participants were provided with coffee, while the other half were not.
The results?
The participants with coffee had a generally positive outlook on the conversations. They contributed greatly and even brought up the group’s performance.
What does this mean?
Well:
It shows us that coffee does more than just keep us alert. It makes us more amicable, friendly, and social.
Conclusion
There you have it…
A few awesome reasons why coffee makes you feel good. And, if you ask me, the science behind it is quite remarkable.
In a nutshell, coffee is not only good for your health but also great for your performance, social skills, and mood enhancement.
Now:
One thing you must remember is that coffee isn’t just about the caffeine.
Its euphoric effects come from a myriad of compounds that work together to deliver the “feel-good” qualities of coffee.
These compounds affect your coffee’s:
- Taste/flavor
- Aroma
- Effectiveness
- As well as overall health benefits
That said:
Do you have any questions or feedback you’d like to share? Let me know your thoughts in the comment section below.


